Who
Phill Gross, owner, and Mike Solimano, CEO of Killington and Pico, Vermont
Recorded on
July 10, 2025
About Killington
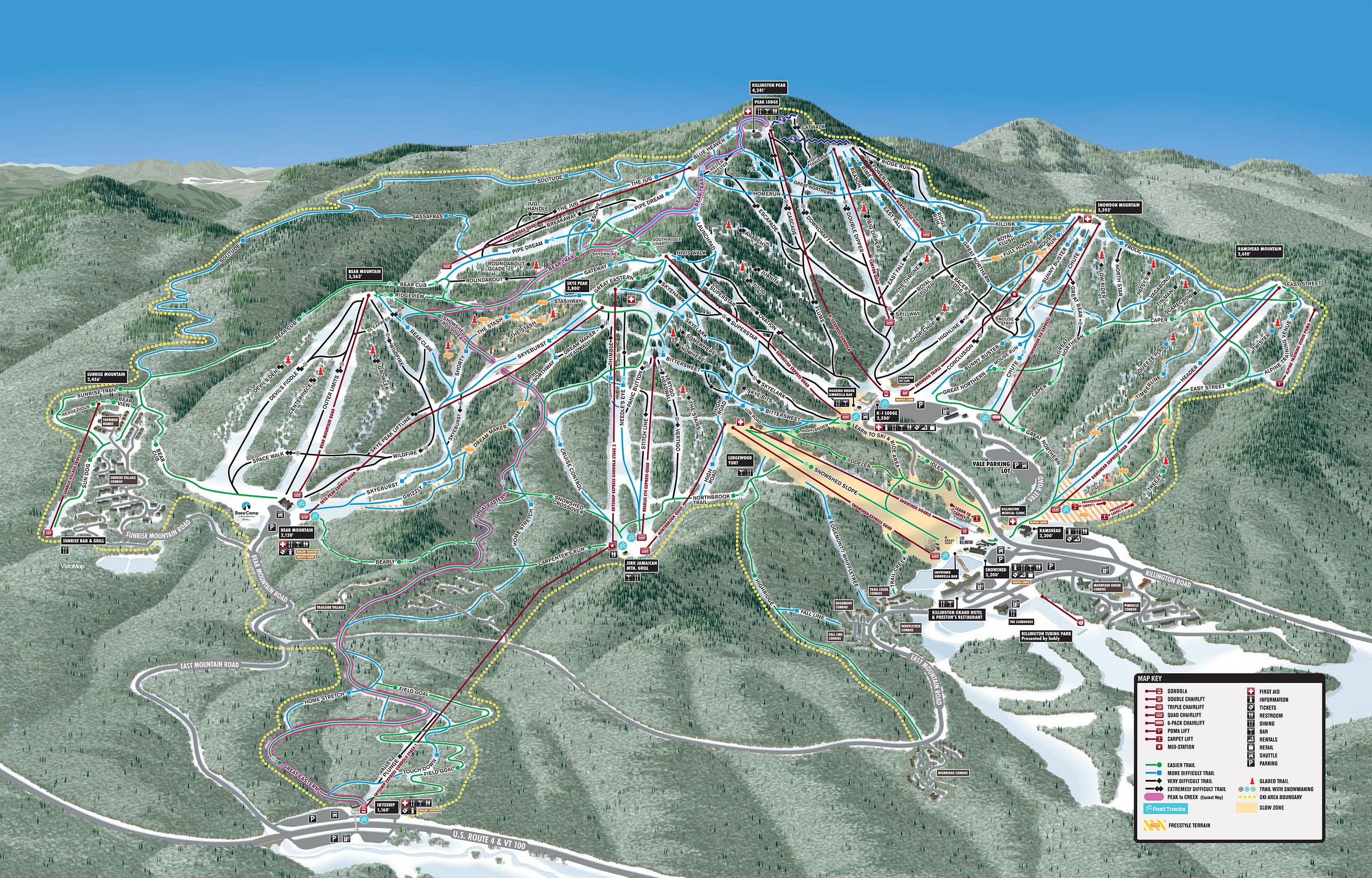
Click here for a mountain stats overview
Owned by: Phill Gross and team
Located in: Killington, Vermont
Year founded: 1958
Pass affiliations: Ikon Pass: 5 or 7 combined days with Pico
Reciprocal partners: Pico access is included on all Killington passes
Closest neighboring ski areas: Pico (:12), Saskadena Six (:39), Okemo (:40), Quechee (:44), Ascutney (:55), Storrs (:59), Harrington Hill (:59), Magic (1:00), Whaleback (1:02), Sugarbush (1:04), Bromley (1:04), Middlebury Snowbowl (1:08), Arrowhead (1:10), Mad River Glen (1:11)
Base elevation: 1,165 feet at Skyeship Base
Summit elevation: 4,142 feet at top of K-1 gondola (hike-to summit of Killington Peak at 4,241 feet)
Vertical drop: 2,977 feet lift-served, 3,076 hike-to
Skiable Acres: 1,509
Average annual snowfall: 250 inches
Trail count: 155 (43% advanced/expert, 40% intermediate, 17% beginner)
Lift count: 20 (2 gondolas, 2 six-packs, 4 high-speed quads, 5 fixed-grip quads, 2 triples, 1 double, 1 platter, 3 carpets - view Lift Blog’s inventory of Killington’s lift fleet; Killington plans to replace the Snowdon triple with a fixed-grip quad for the 2026-27 ski season)
History: from New England Ski History
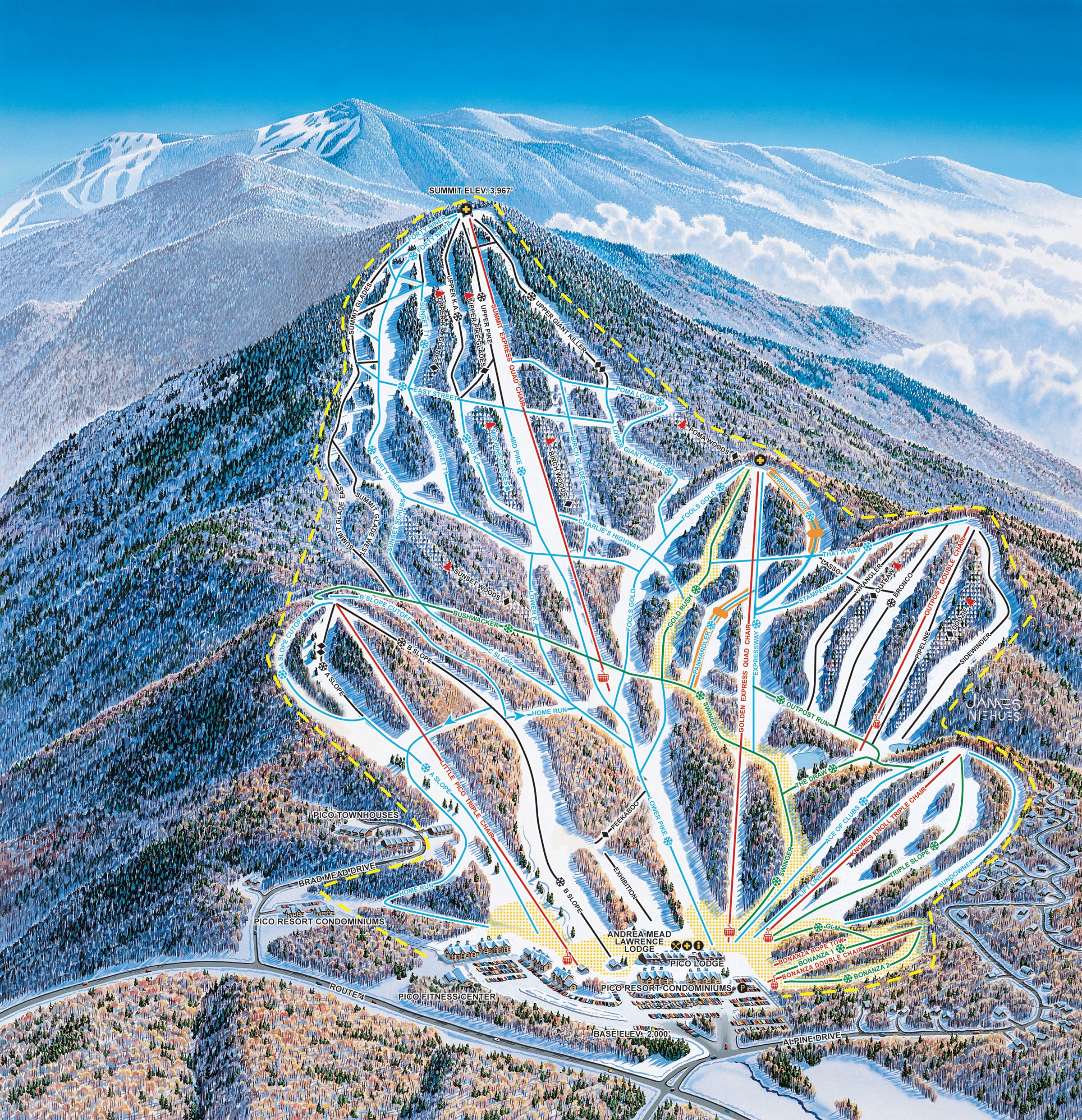
About Pico
Click here for a mountain stats overview
Owned by: Phill Gross and team
Located in: Mendon, Vermont
Year founded: 1934
Pass affiliations: Ikon Pass: 5 or 7 combined days with Killington
Reciprocal partners: Pico access is included on all Killington passes; four days Killington access included on Pico K.A. Pass
Closest neighboring ski areas: Killington (:12), Saskadena Six (:38), Okemo (:38), Quechee (:42), Ascutney (:53), Storrs (:57), Harrington Hill (:55), Magic (:58), Whaleback (1:00), Sugarbush (1:01), Bromley (1:00), Middlebury Snowbowl (1:01), Mad River Glen (1:07), Arrowhead (1:09)
Base elevation: 2,000 feet
Summit elevation: 3,967 feet
Vertical drop: 1,967 feet
Skiable Acres: 468
Average annual snowfall: 250 inches
Trail count: 58 (36% advanced/expert, 46% intermediate, 18% beginner)
Lift count: 7 (2 high-speed quads, 2 triples, 1 doubles, 2 carpets - view Lift Blog’s inventory of Pico’s lift fleet)
History: from New England Ski History

Why I interviewed them
The longest-tenured non-government ski area operator in America, as far as I know, is the Seeholzer family, owner-operators of Beaver Mountain, Utah since 1939. Third-generation owner Travis Seeholzer came on the pod a few years back to trace the eight-decade arc from this dude flexing 10-foot-long kamikaze boards to the present:
Just about every ski area in America was hacked out of the wilderness by Some Guy Who Looked Like That. Dave McCoy at Mammoth or Ernie Blake at Taos or Everett Kircher at Boyne Mountain, swarthy, willful fellows who flew airplanes and erected rudimentary chairlifts in impossible places and hammered together their own baselodges. Over decades they chiseled these mountains into their personal Rushmores, a life’s work, a human soul knotted to nature in a built place that would endure for generations.
It’s possible that they all imagined their family name governing those generations. In the remarkable case of Boyne, they still do. But the Kirchers and the Seeholzers are ski-world exceptions. Successive generations are often uninterested in the chore of legacy building. Or they try and say wow this is expensive. Or bad weather leads to bad financial choices by our cigar-smoking, backhoe-driving, machete-wielding founder and his sons and daughters never get their chance. The ski area’s deed shuffles into the portfolio of a Colorado Skico and McCoy fades a little each year and at some point Mammoth is just another ski area owned by Alterra Mountain Company.
It’s tempting to sentimentalize the past, to lament skiing’s macro-transition from gritty network of founder-kingpin fifes to set of corporate brands, to conclude that “this generation” just doesn’t have the tenacity of a Blake or a McCoy. But the America where a fellow could turn up with a dump truck and a chainsaw and flatten raw forest into a for-profit business with minimal protest is gone. Every part of the ski ecosystem is more regulated, complicated, and expensive than it’s ever been. The appeal of running such a machine - and the skillset necessary to do so - is entirely different from that of sculpting your own personal snow Narnia from scratch.
We will always have family-owned ski areas (we still have hundreds), and an occasional modern founder-disruptor like Mount Bohemia’s Lonie Glieberman will materialize like a new X-man. But ski conglomerates have probably always been inevitable, and are probably largely the industry’s future. They are best suited, in most cases, to manage, finance, and maintain the vast machinery of our largest ski centers (and also to create a ski landscape in which not all ski area operators are Some Guy Who Looked Like That).
Killington demonstrates this arc from rambunctious founder to corporate vassal as well as any mountain in the country. Founded in 1958 by the wily and wild Pres Smith, the ski area’s parent company, Sherburne Corp., bought Sunday River, Maine in 1973 and Mount Snow, Vermont in 1977. The two Vermont mountains became S-K-I in 1984, bought five more ski areas, and merged with four-resort LBO in 1996 to become the titanic American Skiing Company. Unfortunately ASC turned out to be skiing’s Titanic, and one of the company’s last acts before dissolution was to sell Killington and Pico to Utah-based Powdr in 2007.
The Beast had been tamed, at least on paper. Corporate ownership of some sort felt as stapled to the mountain as Killington’s 3,000 snowguns. And mostly, well, it didn’t matter. Other than Powdr’s disastrous attempts to shorten the resort’s famously long seasons, Killington never lost its feisty edge. Over the decades the ski area modernized, masterplanned, and shed skier volume while increasing its viability as a business. Modern Killington wasn’t the kingdom of a charismatic and ever-present founder, but it was a pretty good ski area.
And then, suddenly, shockingly, Powdr sold both Killington and Pico last August. And they didn’t sell the ski areas to Vail or Alterra or Boyne or to anyone who owned any ski areas at all. Instead, a group of local investors - led by Phill Gross and Michael Ferri, longtime Killington homeowners who ran a variety of non-ski-related businesses - bought the mountains. After 51 years as part of a multi-mountain ownership group, Killington (its relationship to neighboring Pico notwithstanding), was once again independent.
It was all so improbable. Out-of-state operators had purchased five of Vermont’s large ski areas in recent years: Colorado-based Vail Resorts bought Stowe in 2017, Okemo in 2018, and Mount Snow in 2019; Denver-based Alterra claimed Sugarbush in 2019; and Utah-based Pacific Group Resorts added Jay Peak to their small portfolio in 2022. Very few ski areas have ever entered the corporate matrix and re-emerged as independents. Grand Targhee, Wyoming; Waterville Valley, New Hampshire; and Mountain Creek, New Jersey (technically owned by multimountain operator Snow Partners) are exceptions spun off from larger companies. But mostly, once a larger entity absorbed a ski area, it stays locked in the multimountain universe forever.
So what would this mean? For the largest and busiest mountain in the eastern United States to be independent? Did this, along with Powdr’s intentions to sell Mount Bachelor (since rescinded), Eldora (sale in process), and Silver Star (no update), mark a reversal in the consolidation trend that had gathered 30 percent of America’s ski areas under the umbrella of a multi-mountain operator? Did Killington’s group of wealthy-but-not-Bezos-wealthy investors set an alternate blueprint for large-mountain ownership, especially when considered alongside the sale of Jackson Hole to a similar group the year before? Had the Ikon Pass – that harbinger of mass-market pass domination that had forced the we-better-join-them sales of Crystal Mountain, Washington and Sugarbush – inadvertently become a reliable revenue pipeline that made independence more viable? And would Killington, well-managed and constantly improving, backslide under cowboy owners who want to Q-Burke the place in their image?
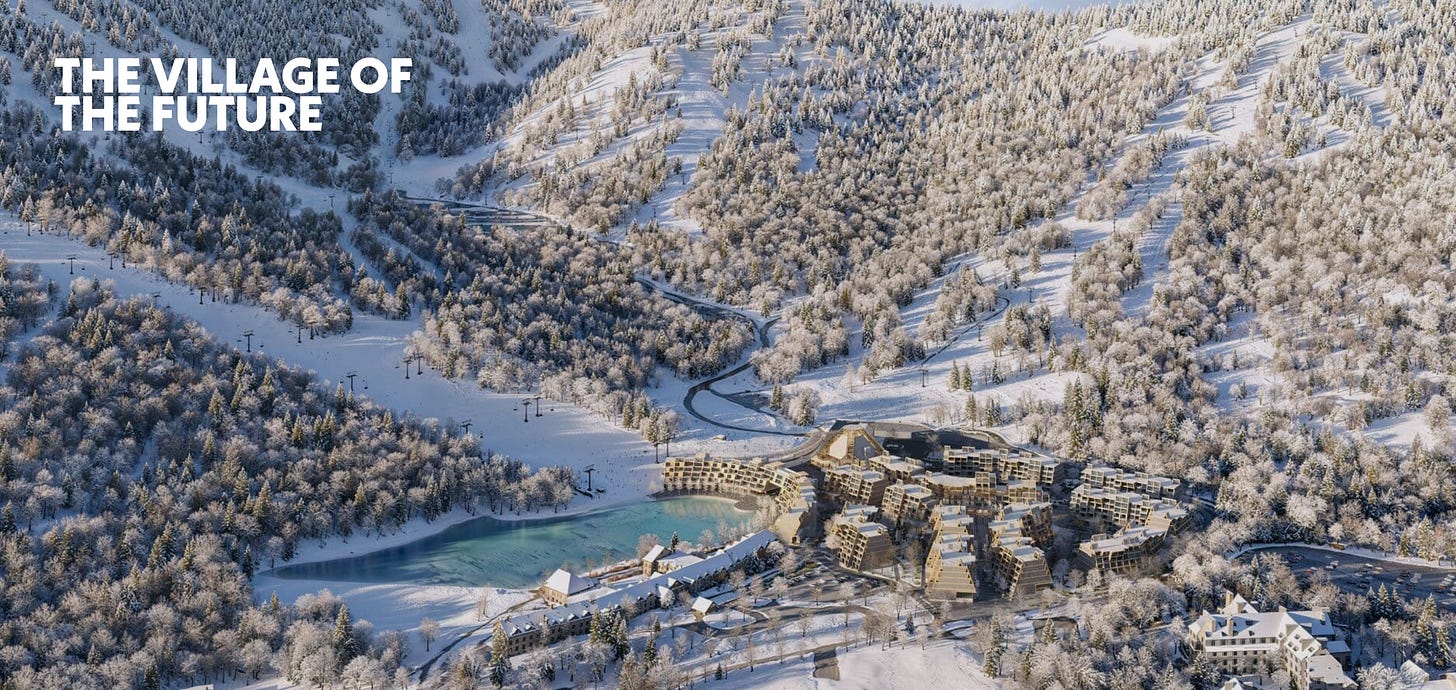
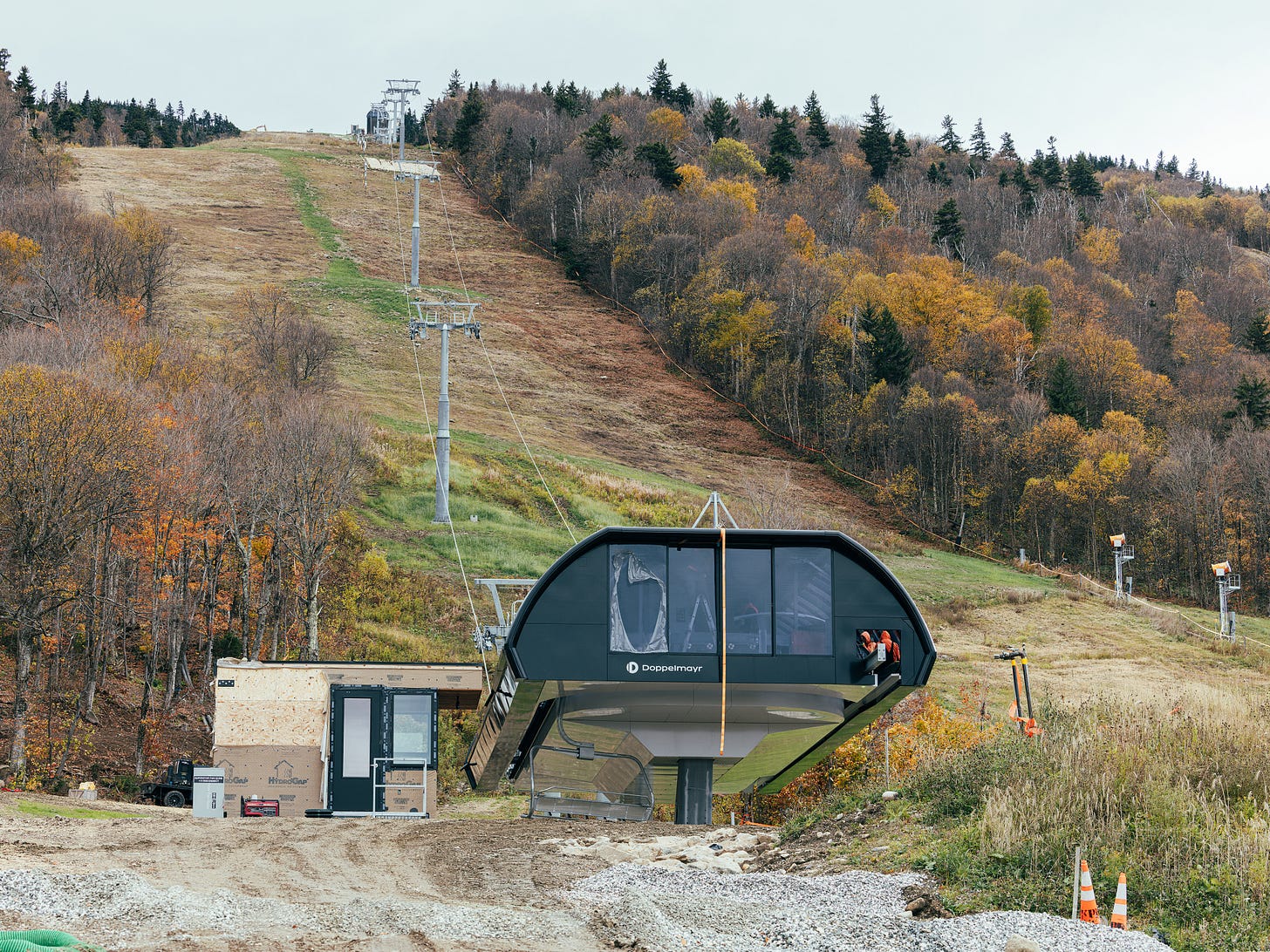
We’re a year in now, and we have some clarity on these questions, along with two new chairlifts (Superstar this year, Snowdon next), 1,000 new snowguns, a revitalized Skyeship Gondola, and progressing plans on the East’s first true ski village. Locals seem happy, management seems happy, the owners seem happy. Easy enough, Gross points out in our interview, when winter hits deep like the last one did. But can we keep the party going indefinitely? It was time for a check-in.
What we talked about
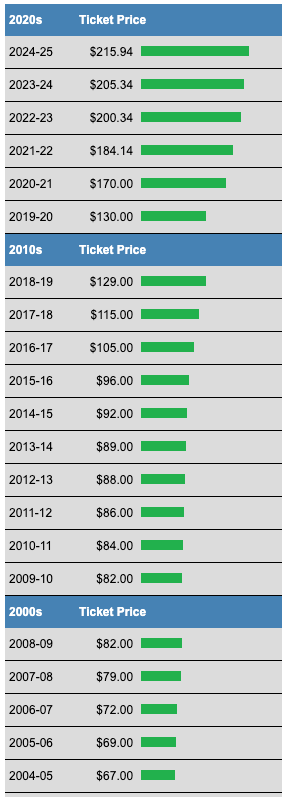
A strong first winter under independent ownership; what spring skiing off Canyon lift told us about the importance of Superstar; “it’s an incredibly complex operation”; letting the smart people do their jobs; Killington’s surprise spin-off from a multi-mountain operator; “our job is to keep the honeymoon going”; Superstar’s six-pack upgrade; why six-packs are probably Killington’s lift-upgrade future; why Pico is demolishing the Bonanza lift for a covered carpet; why Superstar won’t have bubbles; where bubbles might make sense in a future lift; why ski areas can no longer run snowmaking under newly constructed chairlifts; why Superstar is a Doppelmayr machine after Killington installed a brand-new Leitner-Poma six at Snowdon in 2018; long- and short-term Superstar impacts to Killington’s long season; long-term thoughts around early-season walkway access to North Ridge; Skyeship Gondola upgrades, including $5 million in new cabins; what 1,000 new snowguns means in practice; why Killington sold the Wobbly Barn; considering Killington as a business and investment; how Killington is a different financial beast from other Vermont ski areas; how close Killington was to going unlimited on Ikon Pass; Phill’s journey to buying Killington; Devil’s Fiddle and why sometimes things that don’t make sense financially make sense anyway; “we want to own this for generations to come”; a village layout and timeline update – “we want to make sure that this is something that’s additive to the ski experience” even if you don’t own within it; “Great Gulf wants this [village] to be competitive for the western resorts”; “we don’t want to change what Pico is”; how piping water over from Killington has reinvigorated and stabilized Pico; why Killington and Pico remained on Ikon Pass post-sale and probably will for the foreseeable future; is Ikon helping big ski areas stay independent?; Killington’s steady rise in lift ticket prices; future lift upgrades and why the Snowdon Triple is next up for a replacement.

What I got wrong
File “opinionation” under LOL I’m Dumb Talking Is Hard
I said that former Killington owner Powdr had “just sold” Eldora, but that’s not accurate: in July, the town of Nederland, Colorado, announced their intent to purchase the ski area. The sales process is ongoing.
Podcast Notes
On previous Killington pods
On Gross’ purchase of Killington and Pico
On ANSI chairlift standards
We get a bit in the weeds with a reference to “ANSI standards” for chairlifts. ANSI is the American National Standards Institute, a nonprofit organization that sets voluntary but widely adopted standards for everything from office furniture to electrical systems to safety signage in the United States. The ANSI standard for lifts, according to a blog post describing the code’s 2022 update, is “developed by the National Ski Areas Association (NSAA), [and] establishes standard requirements for the design, manufacture, construction, operation, and maintenance of passenger ropeways.”
On Killington’s long seasons
Killington often opens in October (though it has not done so since 2018), and closes in June (three straight years before a deliberately truncated 2024-25 season to begin demolition of the Superstar chair). List of Killington open and close dates since 1987-88.
On Win Smith and Killington and Sugarbush
On Killington’s village
The East needs more of this: