Who
Erik Lambert, Co-Founder of Bluebird Backcountry, Colorado and founder of Bonfire Collective
Recorded on
April 8, 2025
About Bluebird Backcountry
Located in: Just east of the junction of US 40 and Colorado 14, 20-ish miles southwest of Steamboat Springs, Colorado
Years active: 2020 to 2023
Closest neighboring U.S. ski areas: Steamboat (:39), Howelsen Hill (:45),
Base elevation: 8,600 feet
Summit elevation: 9,845 feet
Vertical drop: 1,245 feet
Skiable acres: 4,200-plus acres (3,000 acres guided; 1,200-plus acres avalanche-managed and ski-patrolled)
Average annual snowfall: 196 inches
Lift fleet: None!
Why I interviewed him
First question: why is the ski newsletter that constantly reminds readers that it’s concerned always and only with lift-served skiing devoting an entire podcast episode to a closed ski area that had no lifts at all? Didn’t I write this when Indy Pass added Bluebird back in 2022?:
Wait a minute, what the fuck exactly is going on here? I have to walk to the fucking top? Like a person from the past? Before they invented this thing like a hundred years ago called a chairlift? No? You actually ski up? Like some kind of weird humanoid platypus Howard the Duck thing? Bro I so did not sign up for this shit. I am way too lazy and broken.
Yup, that was me. But if you’ve been here long enough, you know that making fun of things that are hard is my way of making fun of myself for being Basic Ski Bro. Really I respected the hell out of Bluebird, its founders, and its skiers, and earnestly believed for a moment that the ski area could offer a new model for ski area development in a nation that had mostly stopped building them:
Bluebird has a lot of the trappings of a lift-served ski area, with 28 marked runs and 11 marked skin tracks, making it a really solid place to dial your uphill kit and technique before throwing yourself out into the wilderness.
I haven’t really talked about this yet, but I think Bluebird may be the blueprint for re-igniting ski-area development in the vast American wilderness. The big Colorado resorts – other than Crested Butte and Telluride – have been at capacity for years. They keep building more and bigger lifts, but skiing needs a relief valve. One exists in the smaller ski areas that populate Colorado and are posting record business results, but in a growing state in a finally-growing sport, Bluebird shows us another way to do skiing.
More specifically, I wrote in a post the following year:
Bluebird fused the controlled environment and relative safety of a ski area with the grit and exhilaration of the uphill ski experience. The operating model, stripped of expensive chairlifts and resource-intensive snowmaking and grooming equipment, appeared to suit the current moment of reflexive opposition to mechanized development in the wilderness. For a moment, this patrolled, avalanche-controlled, low-infrastructure startup appeared to be a model for future ski area development in the United States. …
If Bluebird could establish a beachhead in Colorado, home to a dozen of America’s most-developed ski resorts and nearly one in every four of the nation’s skier visits, then it could act as proof-of-concept for a new sort of American ski area. One that provided a novel experience in relative safety, sure, but, more important, one that could actually proceed as a concept in a nation allergic to new ski area development: no chairlifts, no snowmaking, no grooming, no permanent buildings.
Dozens of American ski markets appeared to have the right ingredients for such a business: ample snow, empty wilderness, and too many skiers jamming too few ski areas that grow incrementally in size but never in number. If indoor ski areas are poised to become the nation’s next-generation incubators, then liftless wilderness centers could create capacity on the opposite end of the skill spectrum, redoubts for experts burned out on liftlines but less enthusiastic about the dangers of touring the unmanaged backcountry. Bluebird could also act as a transition area for confident skiers who wanted to enter the wilderness but needed to hone their uphill and avalanche-analysis skills first. …
Bluebird was affordable and approachable. Day tickets started at $39. A season pass cost $289. The ski area rented uphill gear and set skin tracks. The vibe was concert-tailgate-meets-#VanLife-minimalism-and-chill, with free bacon famously served at the mid-mountain yurt.
That second bit of analysis, unfortunately, was latched to an article announcing Bluebird’s permanent closure in 2023. Co-founder Jeff Woodward told me at the time that Bluebird’s relative remoteness – past most of mainline Colorado skiing – and a drying-up of investors drove the shutdown decision.

Why now was a good time for this interview
Bluebird’s 2023 closure shocked the ski community. Over already? A ski area offering affordable, uncrowded, safe uphill skiing seemed too wedded to skiing’s post-Covid outdoors-hurray moment to crumble so quickly. Weren’t Backcountry Bros multiplying as the suburban Abercrombie and Applebee’s masses discovered the outside and flooded lift-served ski areas? I offered a possible explanation for Bluebird’s untimely shutdown:
There is another, less optimistic reading here. Bluebird may have failed because it’s remote and small for its neighborhood. Or we are witnessing perception bump up against reality. The popular narrative is that we are in the midst of a backcountry resurgence, quantified by soaring gear sales and perpetually parked-out trailheads. Hundreds of skiers regularly skin up many western ski areas before the lifts open. But the number of skiers willing to haul themselves up a mountain under their own power is miniscule compared to those who prefer the ease and convenience of a chairlift, which, thanks to the megapass, is more affordable than at any point in modern ski history.
Ski media glorifies uphilling. Social media amplifies it. But maybe the average skier just isn’t that interested. You can, after all, make your own ice cream or soda or bread, often at considerable initial expense and multiples of the effort and time that it would take to simply purchase these items. A small number of people will engage in these activities out of curiosity or because they possess a craftsman’s zeal for assembly. But most will not. And that’s the challenge for whoever takes the next run at building a liftless ski area.
Still, I couldn’t stop thinking about my podcast conversation the year prior with Lonie Glieberman, founder of the improbable and remote Mount Bohemia. When he opened the experts-only, no-snowmaking, no-grooming freefall zone in Michigan’s Upper Peninsula in 2000, the ski industry collectively scoffed. It will never work, they promised, and for years it didn’t. Boho lost money for a long time. But Glieberman persisted and, through a $99-season-pass strategy and an aggressively curated fist-bump image, Boho now sits at the aspirational pinnacle of Midwest skiing, a pilgrimage spot that is so successful it no longer sells Saturday day-time lift tickets.
Could Bluebird have ascended to similar cult destination given more time? I don’t know. We might never know.
But shortly after Bluebird’s shuttering, Erik Lambert, who co-founded Bluebird with Woodward, reached out to me. He’s since helped with The Storm’s digital-marketing efforts and knows the product well. With two years to process the rapid and permanent unraveling of an enterprise that had for a time consumed his life and passion, he felt ready to tell his version of the Bluebird story. And he asked if we could use The Storm to do it.
What we talked about
How an East Coast kid developed a backcountry obsession; White Grass, West Virginia; the very long starter-kit list for backcountry skiing; Bluebird as backcountry primer; Jackson Hole as backcountry firestarter; why a nation as expansive and wild as the United States has little suitable land for ready ski area development; a 100-page form to secure a four-day Forest Service permit; early Bluebird pilots at Mosquito Pass and Winter Park; a surprising number of beginners, not just to backcountry, but to skiing; why the founders envisioned a network of Bluebirds; why Bluebird moved locations after season one; creating social scaffolding out of what is “inherently an anti-social experience”; free bacon!; 20 inches to begin operating; “we didn’t know if people would actually pay to go backcountry skiing in this kind of environment”; “backcountry skiing was wild and out there, and very few people were doing it”; who Bluebird thought would show up and who actually did – “we were absolutely flummoxed by what transpired”; the good and bad of Bluebird’s location; why none of the obvious abandoned Colorado ski areas worked for Bluebird; “we did everything the right way … and the right way is expensive”; “it felt like it was working”; why financing finally ran out; comparisons to Bohemia; “what we really needed was that second location”; moving on from failure – “it’s been really hard to talk about for a long time”; Bluebird’s legacy – “we were able to get thousands of people their best winter day”; “I think about it every day in one way or another”; the alternate universe of our own pasts; “somebody’s going to make something like this work because it can and should exist”; and why I don’t think this story is necessarily over just yet.
What I got wrong
We mentioned a forthcoming trip to Colorado – that trip is now in the past, and I included GoPro footage of Lambert skiing with me in Loveland on a soft May day.
I heard “New Hampshire” and assigned Lambert’s first backcountry outing to Mount Washington and Tuckerman Ravine, but the trek took place in Gulf of Slides.

Podcast Notes
On White Grass
The Existing facility that most resembles Bluebird Backcountry is White Grass, West Virginia, ostensibly a cross-country ski area that sits on a 1,200-foot vertical drop and attracts plenty of skinners. I hosted founder Chip Chase on the pod last year:
On Forest Service permit boundaries
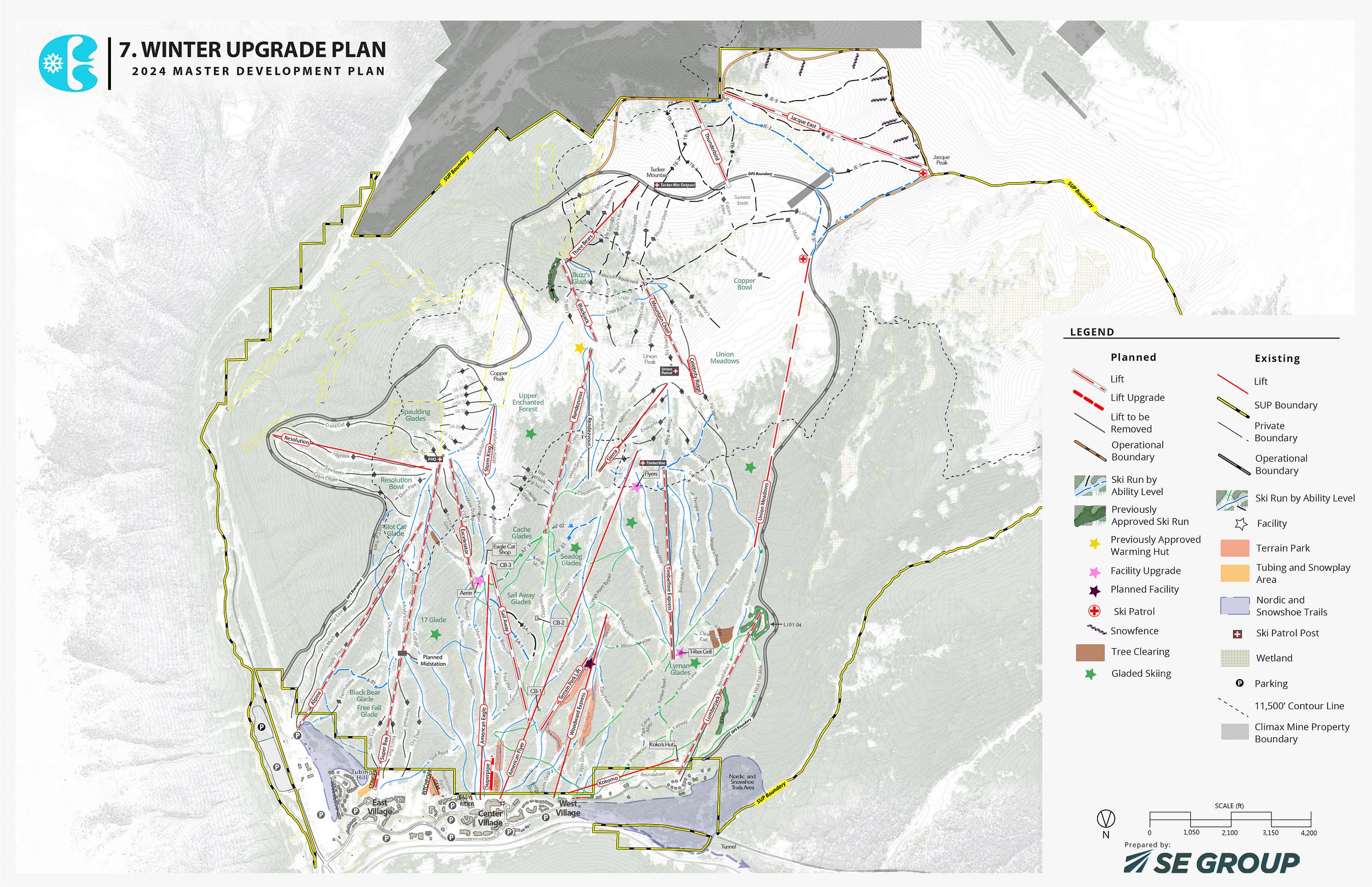
The developed portion of a ski area is often smaller than what’s designated as the “permit area” on their Forest Service masterplan. Copper Mountain’s 2024 masterplan, for example, shows large parcels included in the permit that currently sit outside of lift service:
On Bluebird’s shifting locations
Bluebird’s first season was set on Whiteley Peak:
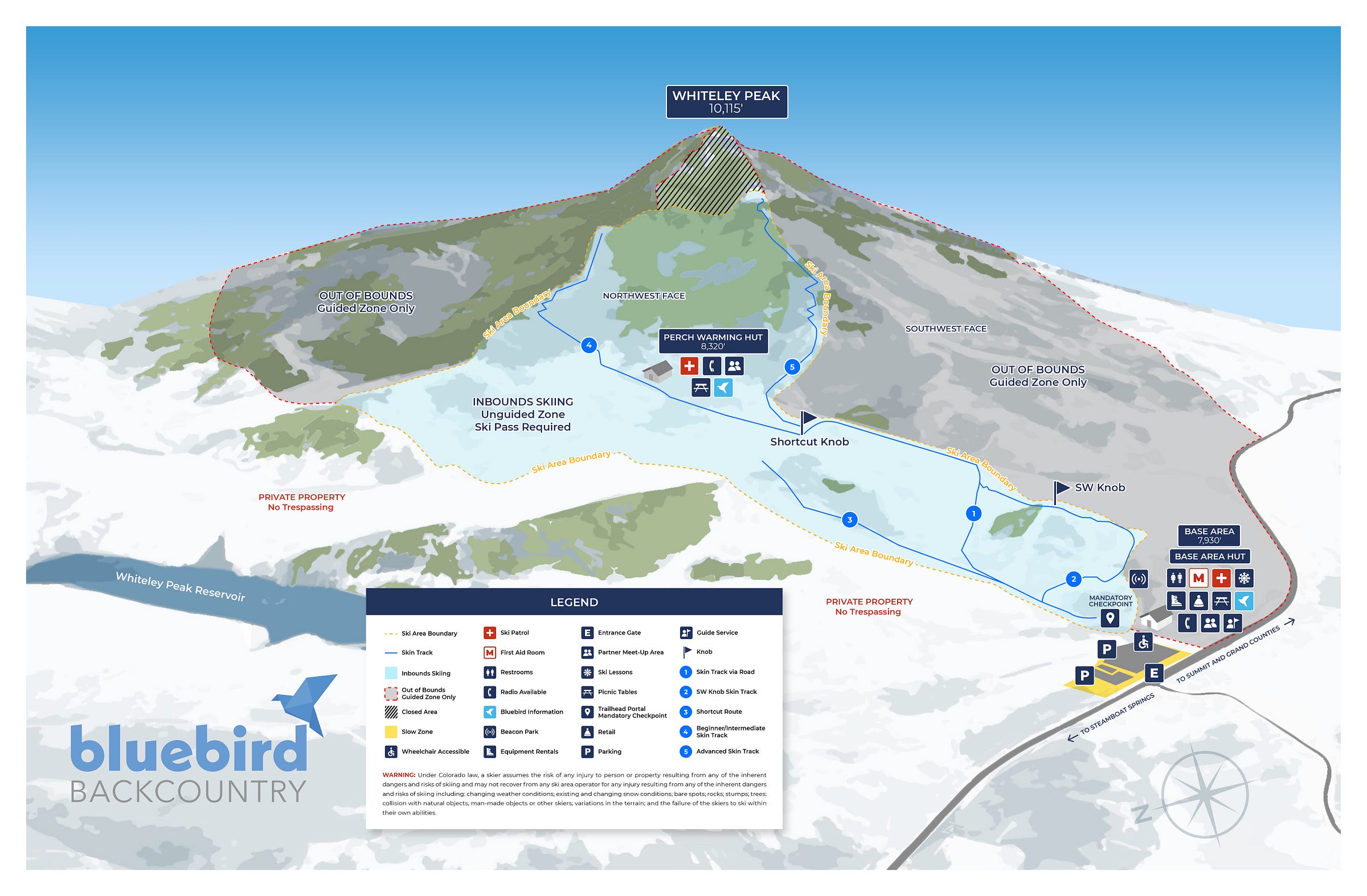
The following winter, Bluebird shifted operations to Bear Mountain, which is depicted in the trailmap at the top of this article. Lambert breaks down the reasons for this move in our conversation.
On breaking my leg in-bounds
Yeah I know, the regulars have heard me tell this story more times than a bear shits under the bridge water, but for anyone new here, one of the reasons I am Skis Inbounds Bro is that I did my best Civil War re-enactment at Black Mountain of Maine three years ago. It’s kind of a miracle that not only did patrol not have to stuff a rag in my mouth while they sawed my leg off, but that I’ve skied 156 days since the accident. This is a testament both to being alive in the future and skiing within 300 yards of a Patrol hut equipped with evac sleds and radios to make sure a fentanyl drip is waiting in the base area recovery room. Here’s the story:
On abandoned Colorado ski areas
Berthoud Pass feels like the lost Colorado ski area most likely to have have endured and found a niche had it lasted into our indie-is-cool, alt-megapass world of 2025. Dropping off US 40 11 miles south of Winter Park, the ski area delivered around 1,000 feet of vert and a pair of modern fixed-grip chairlifts. The bump ran from 1937 to 2001 - Colorado Ski History houses the full story.
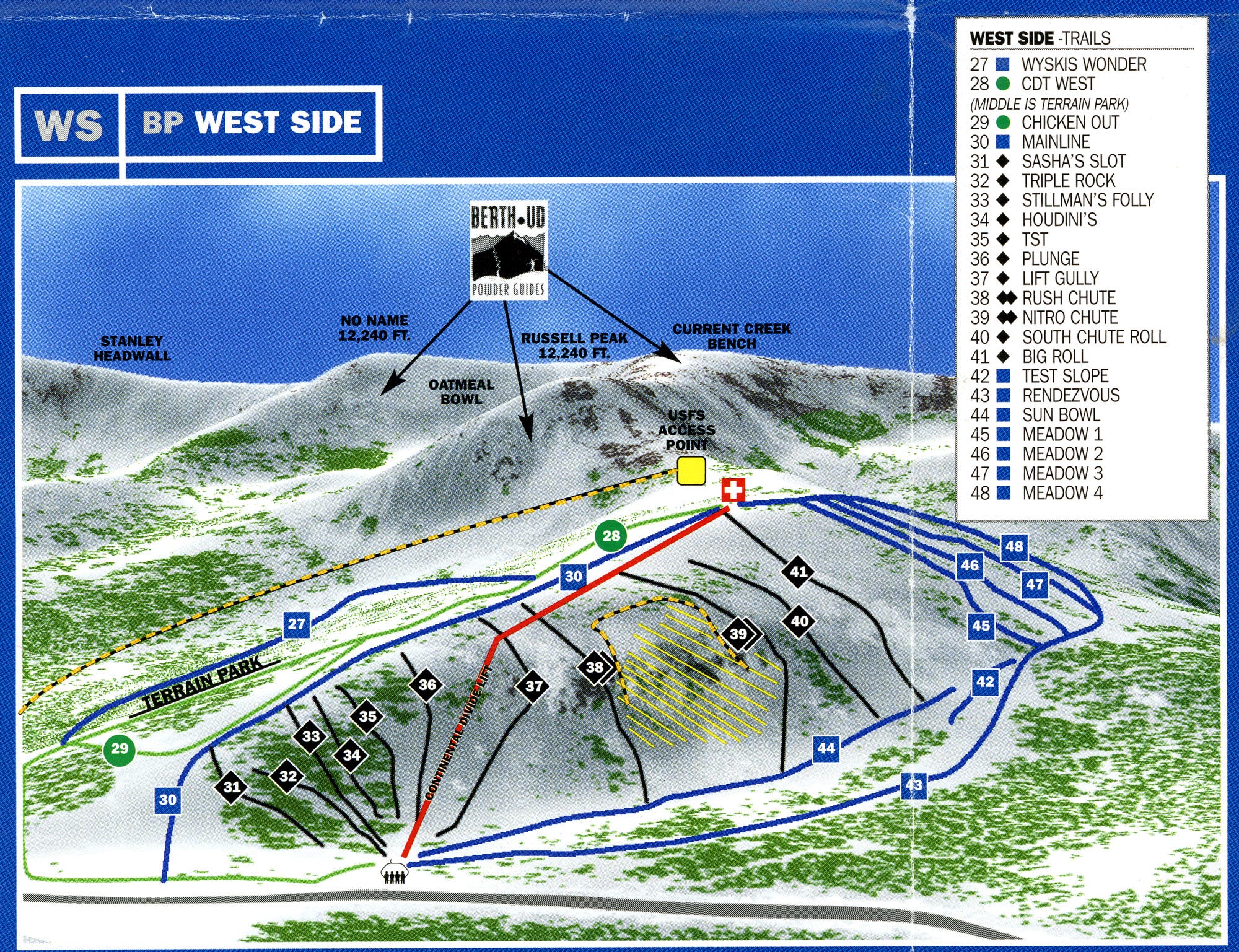
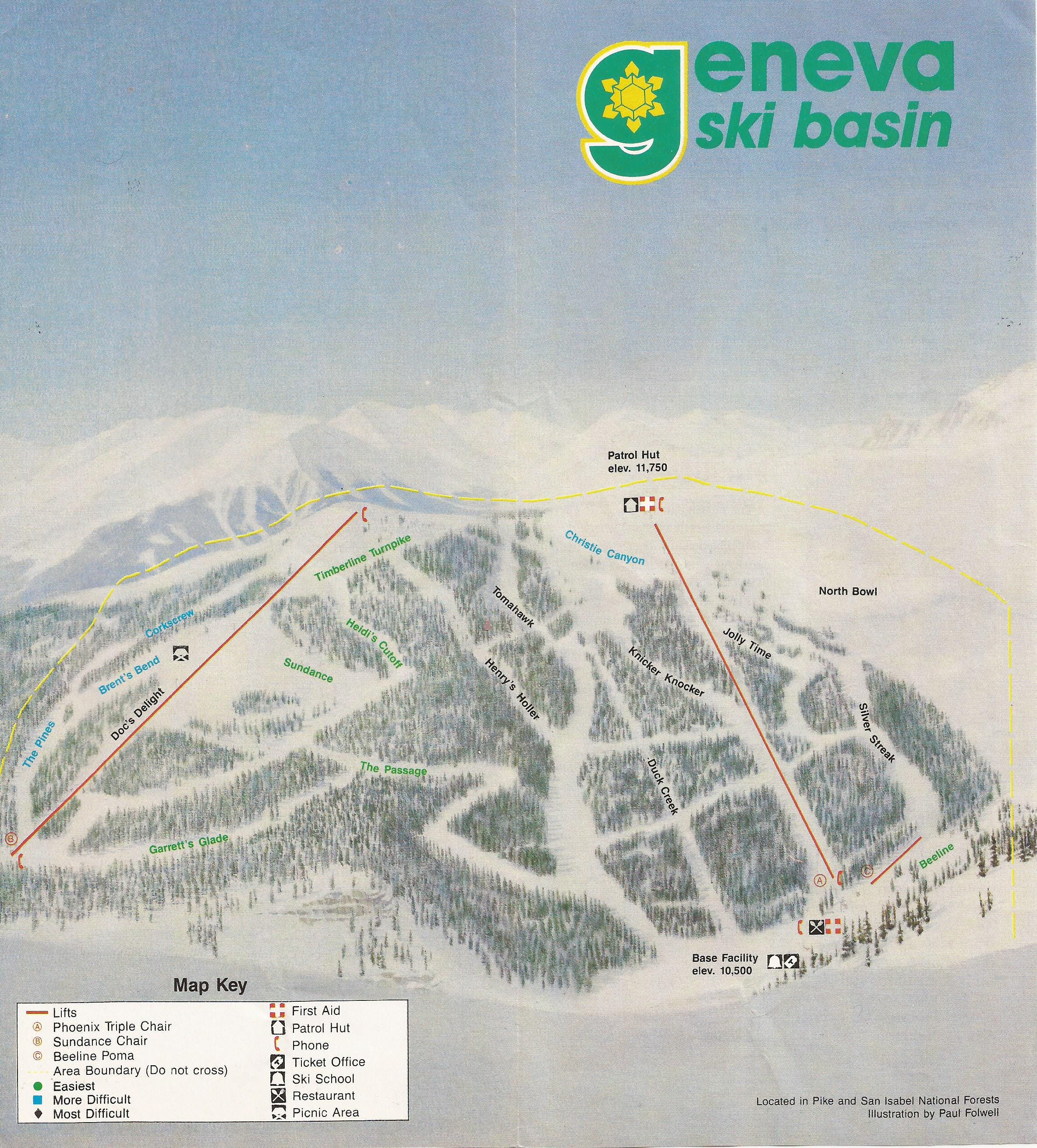
Geneva Basin suffered from a more remote location than Berthoud, and struggled through several owners from its 1963 opening to failed early ‘90s attempts at revitalization (the ski area last operated in 1984, according to Colorado Ski History). The mountain ran a couple of double chairs and surface lifts on 1,250 vertical feet:
I also mentioned Hidden Valley, more commonly known as Ski Estes Park. This was another long-runner, hanging around from 1955 to 1991. Estes rocked an impressive 2,000-foot vertical drop, but spun just one chairlift and a bunch of surface lifts, likely making it impossible to compete as the Colorado megas modernized in the 1980s (Colorado Ski History doesn’t go too deeply into the mountain’s shutdown).

On U.S. Forest Service permits
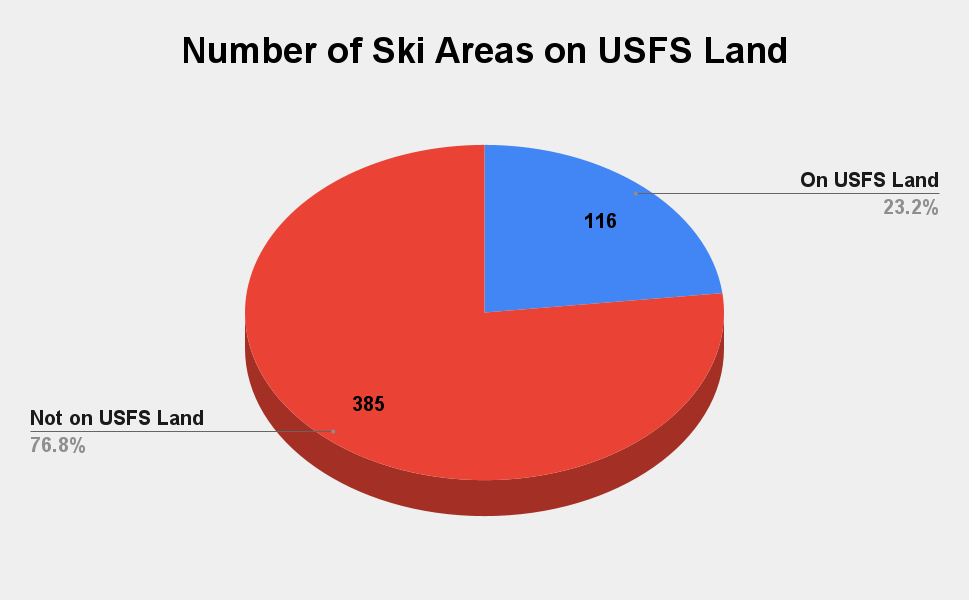
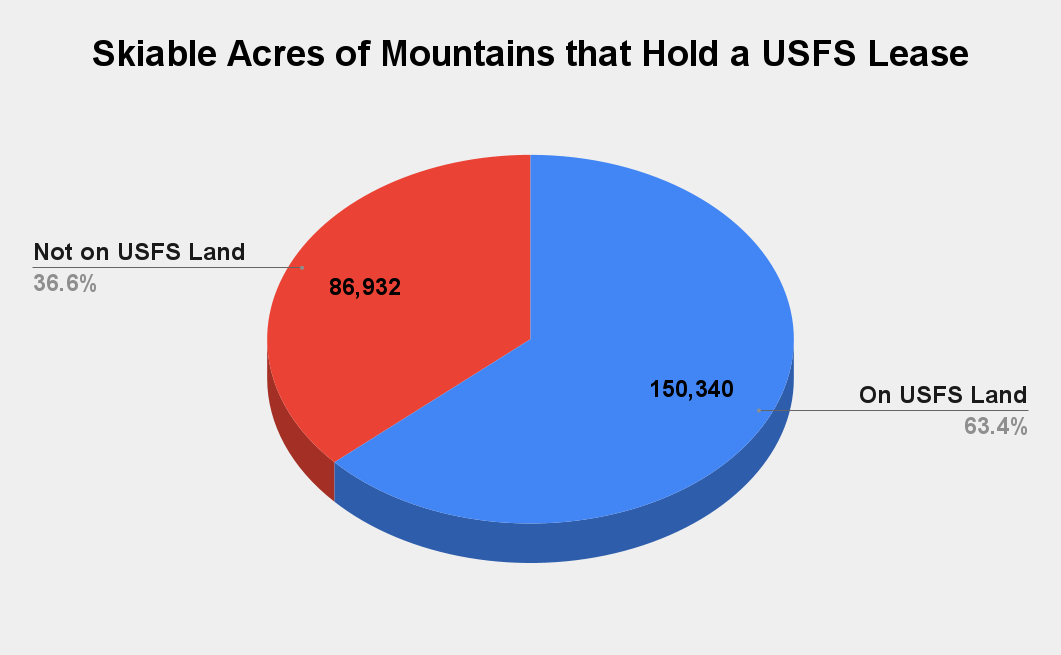
An oft-cited stat is that roughly half of U.S. ski areas operate on Forest Service land. This number isn’t quite right: 116 of America’s 501 active ski areas are under Forest Service permits. While this is fewer than a quarter of active ski areas, those 116 collectively house 63 percentage of American ski terrain.
I broke this down extensively a couple months back: